-

Exploring Careers in Tech for Women
Software engineer Mariana Silva reflects on her journey, saying “I questioned my ability to make it in a field that has been historically male led and influenced…if anything it gave me the push to want to make a difference” (Forbes).
Pursuing studies and a career in any STEM or business field can become discouraging when you notice you’re one of the few women in the room. To thrive in these spaces, resilience is key. That strength often starts with initiatives that encourage and spotlight women who have successfully navigated their respective fields.
Exploring a Potential Career in Tech
In the summers of 2022 and 2023, I participated in Girls Who Code’s self-paced program, a six-week course that gives you introductory lessons on AI and Data Science. These two years opened my eyes to the potential that technology can have in any field. This experience played a pivotal role in my decision to pursue a double major in Data Science alongside Finance.
I highly encourage young women in high school and college to seek out programs that offer hands-on experience in fields they find interesting. Whether in tech, business, or STEM, gaining insight into these subjects can allow for women to grow within multiple fields and develop a diverse skill set. Therefore, taking advantage of resources is crucial.
There are many programs designed to support women in tech, for free or with menial registration fees. Here is a list of 20 organizations dedicated to advancing women in technology:
- Ada Developers Academy
- AnitaB.org
- Black Girls Code
- Girl Develop It
- Girls in Tech
- Girls Who Code
- IEEE Women in Engineering
- Million Women Mentors
- National Center for Women & Information Technology
- Society of Women Engineers
- Switch
- TechLadies
- TechWomen
- Women in Stem
- Women in Tech
- Women in Tech Council
- Women in Technology International
- Women Who Code
- Women Who Tech
Potential Careers in Tech
Tech doesn’t necessarily mean coding all day. The field is highly flexible, making it easy to incorporate many interests. Intersections of tech with fields such as arts, media, business, law, healthcare, psychology, and more have been on the rise lately.
Technology and Business
- FinTech analyst
- Working on cryptocurrency, mobile banking, investment tech
- Product Manager
- Leading strategy and development of products
- Tech Consultant
- Consulting on technological implementation for businesses
Technology and the Arts
- UX/UI Designer
- Combining visual design and coding to create user-friendly interfaces
- Game Designer
- Developing storylines, characters, and mechanics for video games
- Creative Technologist
- Merging art and tech to create interactive installations and digital experiences
Technology and Media/Communication
- Social Media Algorithm Specialist
- Working with AI to optimize social media engagement
- Virtual Production Engineer
- Using real-time rendering, and AI for movie production
- Media Technology Specialist
- Innovates in film production, broadcasting, and digital journalism
Persevering as a Women In Tech
Imposter syndrome and the tendency to compare yourself to others are common struggles in STEM and business. However, these challenges shouldn’t become barriers to success. Instead, remind yourself that breaking through in your field can pave the way for others similar to yourself. Successful women in tech today are doing just so because they allowed themselves to grow, explore their interests, and take advantage of available resources.
If you’re considering a career in tech, do not hesitate to start. Build your confidence by putting yourself in spaces that let you learn.
Citations:
White, Sarah, et al. “20 Organizations Advancing Women in Tech.” CIO, 7 Mar. 2025, www.cio.com/article/215709/16-organizations-for-women-in-tech.html.
Cole, Byron. “Women Empowering Tech: Inspiring Stories of Success and Impact.” Forbes, Forbes Magazine, 20 Sept. 2023, www.forbes.com/sites/byroncole/2023/09/13/women-empowering-tech-inspiring-stories-of-success-and-impact/.
“Creative Technology Careers: Pathways and Opportunities.” Creative Technology Careers: Exploring Opportunities & Pathways – Meadows School of the Arts, SMU, 5 July 2023, www.smu.edu/meadows/newsandevents/news/2023/careers-in-creative-technology.
Carlton, Genevieve. “Career Guide for Women in Tech: BestColleges.” BestColleges.Com, 28 Feb. 2023, www.bestcolleges.com/careers/career-guide-women-in-tech/.
“The World’s Top 50 Women in Tech.” Forbes, Forbes Magazine, www.forbes.com/top-tech-women/list/#tab:overall. Accessed 25 Mar. 2025.March 29, 2025
-

How has game theory changed with constant development of technology, more specifically, AI?
Game theory is an important concept in economics as it concerns decision-making that is dependent on others’ decisions. Game theory was inspired by the strategies used in poker, and John von Neumann formalized these mathematically. Since then, its uses have broadened, reaching to military strategy during the Cold War. However, it is typically used within the economics of the business world.
Going with the trends of today, artificial intelligence is the new addition to almost every field possible. We will focus on game theory. AI’s introduction to game theory began with IBM’s Deep Blue and Google DeepMind’s Alpha Go. Artificial intelligence was able to simulate using similar mathematical models to economics game theory in these games, showcasing its ability to analyze moves and interactions in scenarios beyond games. AI plays a key role in decision-making, predictive analysis, future predictions, and the implications of game theory.
Within decision-making and analysis, AI is able to predict market trends, and competitor moves, and creates strategies for optimal price and resource allocation. It is able to apply current affairs and the patterns from it to stimulate scenarios using historical and real-time data, and utilize behavioral data from human decision-making, which plays a key role in creating realistic and rational game theory models. The more that AI becomes integrated within each aspect of businesses, the more that real-time data will become available and game theory models can become more accurate, which allows businesses to make complex decisions effectively, and efficiently. However, here arises the question of how ethical is this practice given that information is accessible at all times easily?
Citations:
Game Theory in Economics and Beyond Academic Journal | Samuelson, 2016 | DOI 10.1257/jep.30.4.107
https://www.weforum.org/stories/2015/06/how-has-game-theory-changed-economics/ Website | https://www.weforum.org/stories/2015/06/how-has-game-theory-changed-economics/Game Theory: A Comprehensive Guide Website | Adam Hayes, | https://www.investopedia.com/terms/g/gametheory.asp
December 13, 2024
-

How do government interventions, such as antitrust lawsuits, influence the rate of innovation in monopolistic tech industries?
For monopolies to have an incentive to improve and avoid stagnation in the long run, there needs to be competition. For this reason, government interventions can help to create a competitive environment for monopolistic tech-companies to develop more technology and innovation. The role of antitrust lawsuits can play a huge part in promoting competition. Antitrust lawsuits can restrict market fairness such as price-fixing, unfair contracts, or acquisition of competitors. A prime example of a company acquiring their competition is Facebook acquiring Instagram and WhatsApp. Antitrust laws can have a significant positive impact on innovation by breaking up monopolies to create competitors, encouraging competition, and reducing resource hoarding.
Antitrust laws, however, have negative consequences. There is a loss of economic scale which happens through the breaking up of monopolies because there is a reduction in capital in order for innovations. Another drawback is a disruption to ecosystems. Tech companies are all a part of an integrated ecosystem, and breaking up a monopoly can create many inefficiencies leading to lower innovation. Additionally, restricting acquisitions may be very detrimental to startups, who rely on firms to acquire them as a way to exit the market.
Citations:
Antitrust and Innovation Competition Website | Elinor Hobbs Distinguished Professor of International Business and Professor of Strategy, Kellogg School of Management, Northwestern University. Professor of Law (Courtesy), Pritzker School of Law, Northwestern University, USA & Spulber, Daniel F, | https://academic.oup.com/antitrust/article/11/1/5/6593929
Technological Innovation And Monopolization Website | , 2015 | https://www.justice.gov/archives/atr/technological-innovation-and-monopolizationAntitrust Enforcement and High Technology Markets Website | , 2013 | https://www.ftc.gov/news-events/news/speeches/antitrust-enforcement-high-technology-markets
December 7, 2024
-

How is insurance and healthcare related to the concept of the “lemons problem”?
This concept of “market of lemons” is based on the topic of asymmetric information. Basically, a ‘lemon’ is a product that is defective, and only sellers know that the product is defective. Because of this lack of information, a market failure occurs.
One of the biggest examples is healthcare insurance. Individuals have their personal information about their health and risks, which insurance companies do not have. For example, a person with a chronic illness knows that they will receive higher medical costs, but they will not disclose this fact to insurance companies. Therefore, insurance companies just charge an average premium based on expectations. However, while it is an average premium, low-risk individuals usually opt out of this insurance. When low-risk individuals leave the target market, the risk level rises, and costs for insurance rise.
Younger and healthier people usually don’t choose to buy health insurance. This example can also apply to car insurance; drivers who know they are safe will buy a lower priced insurance, while drivers who know they are prone to accidents will buy a more secure insurance. These are some worldly examples.
How do firms attempt to avoid this problem?
Mandates:
- Some acts like the Affordable Care Act require individuals to opt in for health insurance to ensure that there are still low-risk individuals in the pool, which balances the average risk.
Risk-Based Pricing:
- Insurance companies would need to receive more information on the individual to set an appropriate price.
Group Insurance:
- Many employers use group insurance, which takes the overall risk of that group and there is a balance which is more appropriate and specific to the group.
Government Subsidies
- Insurance companies can receive subsidies to cover high-risk individuals who will not be able to afford insurance.
Incentives:
- Insurance companies can offer more discounts for people who have healthier behaviors.
What is the overall impact of adverse selection in insurance?
If insurance companies need more information on an individual to attempt to solve this problem, is there a breach in privacy?
Citations:
Britannica MoneyWebsite | https://www.britannica.com/money/adverse-selection
Examples of Adverse Selection in the Insurance Industry Website | J.B. Maverick, | https://investopedia.com/articles/insurance/082516/examples-adverse-selection-insurance-industry.aspMarket of Lemons in Healthcare : Networks Course blog for INFO 2040/CS 2850/Econ 2040/SOC 2090 Website | https://blogs.cornell.edu/info2040/2019/12/03/market-of-lemons-in-healthcare/
Does Making Health Insurance Enrollment Easier Cause Adverse Selection? Website | , 2022 | https://www.commonwealthfund.org/blog/2022/does-making-health-insurance-enrollment-easier-cause-adverse-selection
November 16, 2024
-
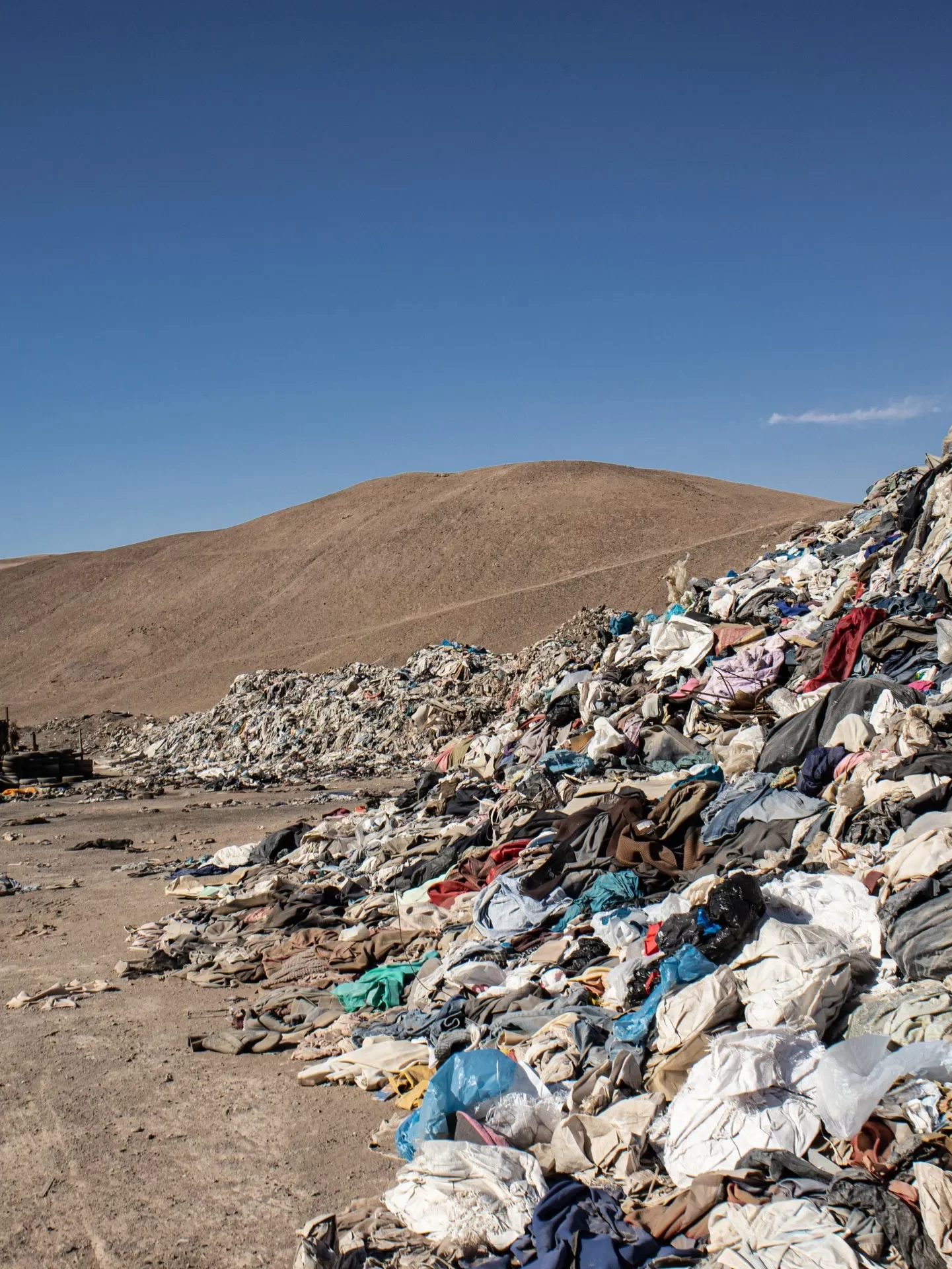

How is fast fashion exemplifying the tragedy of the commons, and what are its externalities?
First, what is the tragedy of the commons? The Tragedy of the commons refers to when people in their self-interest gain access to a public resource and eventually the shared resource is depleted.
Fast fashion is a huge problem nowadays. The production of clothing for fast fashion brands creates textile wastage, and indirectly consumes many common raw materials. The psychology is this: people consume fast fashion with the assumption of an abundance of goods and because there seems to be less financial limitations, their desire to buy increases. Buying one shirt a week can have its effects. Moreover, the majority of people in the world also have this mindset. In turn, the apparel company continues to profit and create more goods, the majority of them following short-term trends, and consuming water, cotton, and raw materials. Overproduction leads to product surplus, offering lower prices, and in turn creating more consumption and later wastage. The depletion of the common materials stated above is the tragedy of the commons. For companies who create these fast fashion products, their common good is labor, humans from Third World countries. As production increases, their labor is exploited and harmed, leading to a depletion and eventually a circle of exploitation.
Negative externalities of fast fashion are harmful. Pollution waste is very prominent and often affects Third World countries. Fashion is produced in large factories and the dangerous working conditions typically spillover into the labor, causing the factory workers to become ill and injured.
The analyzation of these effects raises the question: How can the government begin to regulate fast fashion industries? How can countries come together to address the negative externalities of textile waste?
Citations:
How Fast Fashion Is Destroying the Planet (Published 2019) Website | Tatiana Schlossberg, 2019 | https://www.nytimes.com/2019/09/03/books/review/how-fast-fashion-is-destroying-the-planet.html
Tragedy of the Commons: Examples & Solutions | HBS Online Website | , 2019 | https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/tragedy-of-the-commons-impact-on-sustainability-issuesFeatured: Tragedy of the commons | Textiles wastage in Singapore Website | https://blogs.ntu.edu.sg/hp3203-2018-27/tragedy-of-the-commons/
November 2, 2024
-

How have electric vehicle subsidies accelerated technological growth and the overall economy?
Since electric vehicles are a much cleaner alternative to gas-powered cars, the US Government provides large subsidies to EV producers. Because of this, climate pollution has gone down. American car manufacturers have also seen growth. In 2022, a law in the Inflation Reduction Act gave electric vehicle subsidies to car manufacturers. Under the IRA, car manufactures were more incentivized to produce cleaner technologydue to $7,500 intax credits.In development, they were more likely to take risksin research and invest in good quality materials. As a result, there was more push regarding the advancements of EV batteries, their charging system, and the range in which they can travel. Moreover, these developments have made EVs more valuable, desirable, and affordableto an average consumer.
Regarding technological manufacturing, the policy requires EVs to be assembled in North America and for components to only be sourced from the US or allied countries. This allowed for more growth in production domestically.The domestic growth incentive is another reason for EV growth generally. This leads to the next point being the benefit of economic growthfrom EV subsidies. US EV car manufacturers received higher profits due to more production and demand, and by saving costs from producing domestically. Moreover, due to more production and research, agreater number of jobs have been created.
How have other businesses attempted to maximize the use of their subsidies? How might the monetary amount of subsidies fluctuate if EV demand goes down and there is a problem in production?
Citations:
Pros And Cons Of Subsidizing Electric Vehicles Website | , 2023 | https://ace-usa.org/blog/research/research-environmental-policy/pros-and-cons-of-subsidizing-electric-vehicles/
Study finds electric vehicle subsidies help the climate and automakers – but at a cost Website | https://news.stanford.edu/stories/2024/10/electric-vehicle-subsidies-help-the-climate-u-s-automakers#:~:text=min%20readEconomics-,Electric%20vehicle%20subsidies%20help%20the%20climate%20and%20automakers%2C%20but%20at,have%20purchased%20EVs%20without%20subsidies.October 19, 2024
-
Why was the demand for luxury goods during the pandemic staying the same even after an increase in their prices?
Post pandemic, many high-end luxury brands had a surge in their revenues. The reasoning behind this was because after the pandemic, many people’s point of views shifted on impulsive buying after it became more normalized. Some people also stated that staying in their houses during the pandemic made them long for these luxury items even longer. Online shopping also increased, which also increased impulsive buying because shopping became quicker. The demand for the goods was staying the same even if the prices for items were ridiculously high, showing that this was an inelastic situation. However, what would the price limit be for people to decrease their demand? Also, how was the elasticity for more normal and inferior goods if luxury goods were this inelastic?
Citations: Why luxury goods sales are surging in the pandemic Website | Hillary Chabot, 2022 | https://news.northeastern.edu/2022/01/26/luxury-spending-surge-during-pandemic/
Image citation: Luxury Goods Collage. (n.d.). https://miro.medium.com/v2/resize:fit:1400/1*xuSlRYb1yFbqOrB5PKq7TA.png
September 27, 2024